The most common methods that investors use to know the benefits and risks associated with long-term investments include fundamental analysis, technical analysis, and quantitative analysis.
For long-term investors, what’s attractive are investments offering a greater chance of maximizing their returns over a longer period of time.
In general, that period is at least one year, but many financial experts suggest timeframes of five, ten, or longer years.
One of the biggest advantages of being a long-term investor is the ability to save and invest for big goals requiring long time to achieve the highest rewards.
However, understanding the difference between fundamental, technical, and quantitative analysis is also important.
Fundamental Analysis
Most investors who make long-term investment decisions start with the fundamental analysis of a company, an individual stock, or the market as a whole.
Fundamental analysis is the process of gauging a security’s intrinsic value by examining all aspects of the business or the market.
Tangible assets like land, equipment, or buildings a company owns are reviewed along with intangible assets like trademarks, patents, branding, or intellectual property.
Investors use fundamental analysis not only to assess the broader scope of the stock market but also to review economic factors.
And these factors include the overall strength of the economy and industry sector conditions.
Technical Analysis
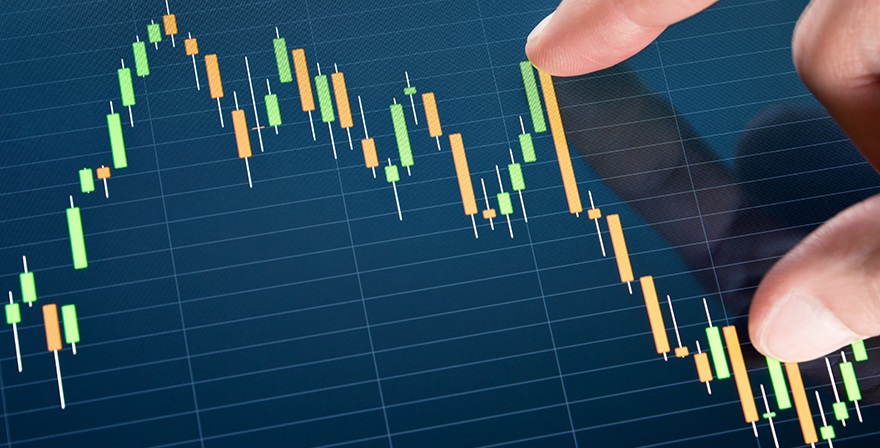
Technical analysis is the process of evaluating securities through statistics. Analysts and investors use data on market activity such as historical returns, stock prices, and volume of trades to make chart patterns in asset movements.
While fundamental analysis shows the intrinsic value of a security or specific market, technical analysis tries to provide some insight on the future activity of securities or the market as a whole.
Investors and financial analysts using technical analysis believe strongly the future performance of the security can be found if we review the patterns based on the data about the price’s past performance.
Analysts use data from short durations of time to develop the patterns used to predict securities or market movements. This is opposed to fundamental analysts that rely on information spanning years.
Because the data collection in this analysis has short durations, many investors tend to use this method more in short-term trading.
On the other hand, the technical analysis technique can be a sharp tool in evaluating long-term investments when used in conjunction with the fundamental analysis technique in investing.
Quantitative Analysis
The evaluation of the historical performance of a company or broader industry is usually done via quantitative analysis.
Investors perform quantitative analysis using simple financial ratio calculations like earnings per share (EPS) or more complicated calculations like discounted cash flow (DCF).
The results of quantitative analysis offer insights into the valuation or past performance of a specific security or market.
However, the quantitative analysis technique is not usually used as a standalone method for evaluating long-term investments.
Rather, quantitative analysis is used along with fundamental and technical analysis to find the potential advantages and risks of investment decisions.
The key to success is awareness. That’s why you need to go and check Finance Brokerage educational websites available. And you can choose the one that suits you the best in the Online Trading Courses offered.